Findings implicate a specific type of immune cell behind heterotopic ossification--and present a potential target for treatment.
5:00 AM
Author |

Hip replacements, severe burns, spinal cord injuries, blast injuries, traumatic brain injuries—these seemingly disparate traumas can each lead to a painful complication during the healing process called heterotopic ossification. Heterotopic ossification is abnormal bone formation within muscle and soft tissues, an unfortunately common phenomenon that typically occurs weeks after an injury or surgery. Patients with heterotopic ossification experience decreased range of motion, swelling and pain.
Currently, "there's no way to prevent it and once it's formed, there's no way to reverse it," says Benjamin Levi, M.D., Director of the Burn/Wound/Regeneration Medicine Laboratory and Center for Basic and Translational Research in Michigan Medicine's Department of Surgery. And while experts suspected that heterotopic ossification was somehow linked to inflammation, new U-M research explains how this happens on a cellular scale—and suggests a way it can be stopped.
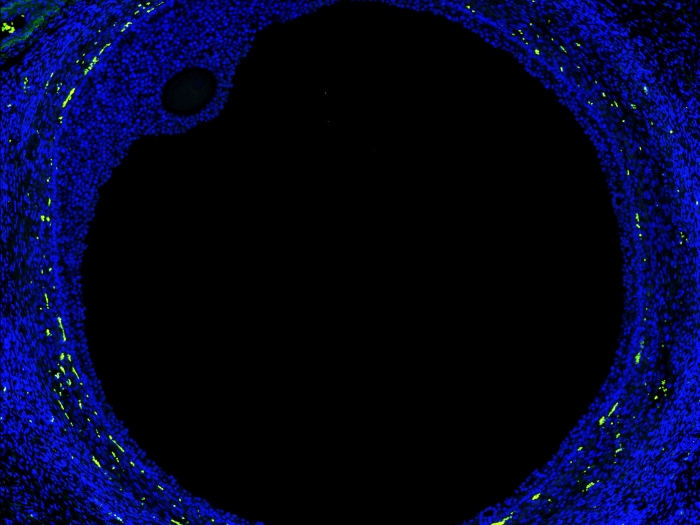
To help explain how the healing process goes awry in heterotopic ossification, the research team, led by Levi, Michael Sorkin, M.D. and Amanda Huber, Ph.D., of the Department of Surgery's section of plastic surgery, took a closer look at the inflammation process in mice. Using tissue from injury sites in mouse models of heterotopic ossification, they used single cell RNA sequencing to characterize the types of cells present. They confirmed that macrophages were among the first responders and might be behind aberrant healing.
Macrophages are white blood cells whose normal job is to find and destroy pathogens. Upon closer examination, the Michigan team found that macrophages are more complex than previously thought—and don't always do what they are supposed to do.
"Macrophages are a heterogenous population, some that are helpful with healing and some that are not," explains Levi. "People think of macrophages as binary (M1 vs. M2). Yet we've shown that there are many different macrophage phenotypes or states that are present during abnormal wound healing."
Specifically, during heterotopic ossification formation, the increased presence of macrophages that express TGF-beta leads to an errant signal being sent to bone forming stem cells.
For now, the only way to treat heterotopic ossification is to wait for it to stop growing and cut it out which never completely restores joint function. This new research suggests that there may be a way to treat it at the cellular level. Working with the lab led by Stephen Kunkel, Ph.D. of the Department of Pathology, the team demonstrated that an activating peptide to CD47, p7N3 could alter TGF-beta expressing macrophages, reducing their ability to send signals to bone-forming stem cells that lead to heterotopic ossification.
"During abnormal wound healing, we think there is some signal that continues to be present at an injury site even after the injury should have resolved," says Levi. Beyond heterotopic ossification, Levi says the study's findings can likely be translated to other types of abnormal wound healing like muscle fibrosis.
The team hopes to eventually develop translational therapies that target this pathway and further characterize not just the inflammatory cells but the stem cells responsible for the abnormal bone formation.
The paper is published in the journal Nature Communications. Other U-M authors include: Charles Hwang, William Carson IV, Rajarsee Menon, John Li, Kaetlin Vasquez, Chase Pagani, Nicole Patel, Shuli Li, Noelle D. Visser, Yashar Niknafs, Shawn Loder, Melissa Scola, Dylan Nycz, Katherine Gallagher, Laurie K. McCauley, Shailesh Agarwal, and Yuji Mishina.
Paper Cited: "Regulation of heterotopic ossification by monocytes in a mouse model of aberrant wound healing," Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-14172-4

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!